Summary
Managing Parkinson’s disease in India requires a multifaceted, evidence-driven approach. While medication and surgical advancements are vital, equally important are high-fibre diets, strategic protein intake, antioxidant-rich foods, and adequate hydration. Regular physical activity—walking, yoga, resistance training, dance—preserves mobility and emotional stability. Holistic strategies, including alternative medicine, sleep hygiene, and social engagement, support dignity and independence. Families, caregivers, and support groups form the backbone of lasting patient care. Stay connected to healthcare professionals, monitor symptoms, join patient communities, and adapt daily routines for optimal well-being. Indian patients and families now have more hope and practical resources than ever before to live better with Parkinson’s.
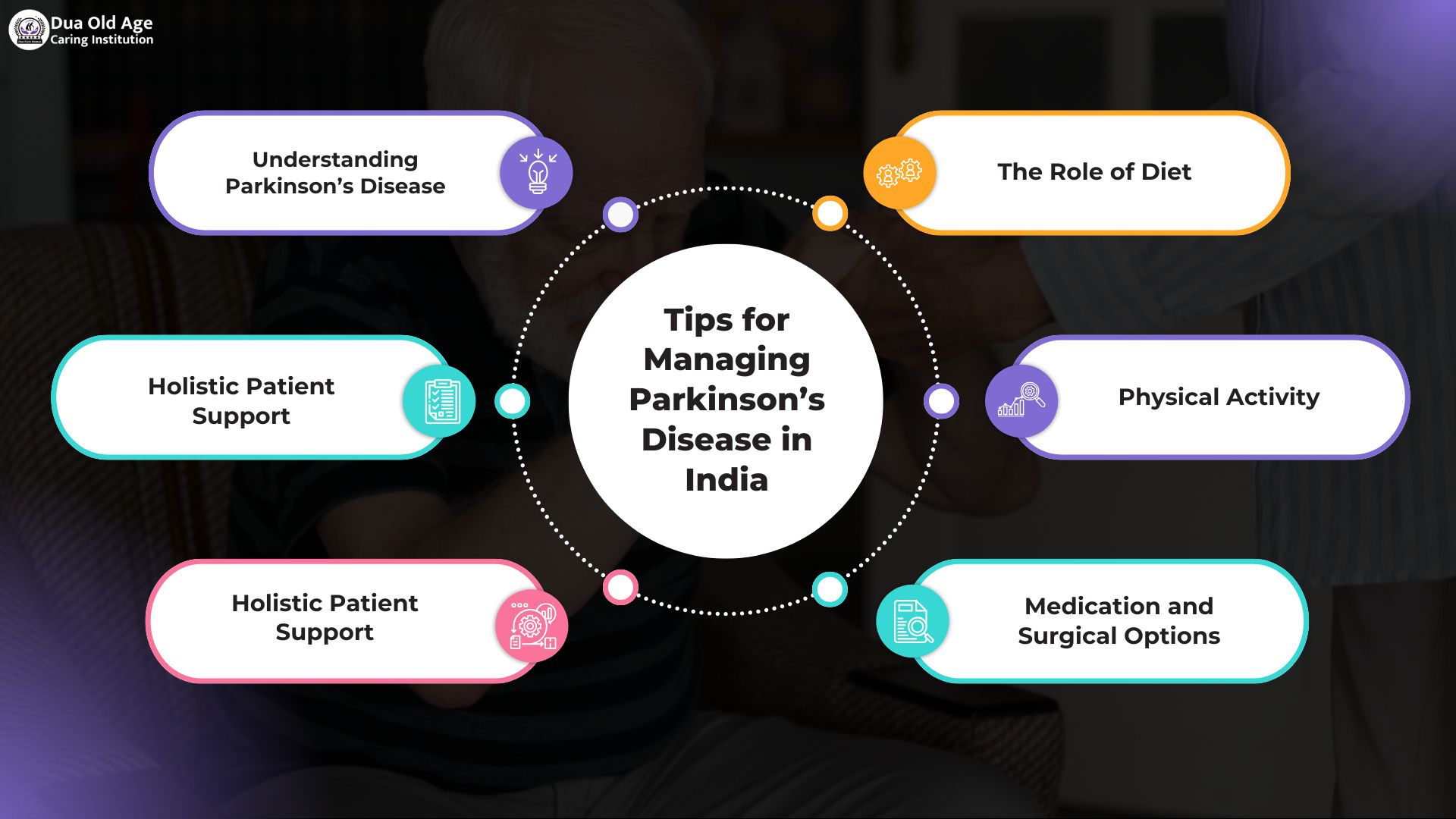
Best Lifestyle Tips for Managing Parkinson’s Disease in India: Diet, Exercise
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting millions worldwide, with growing prevalence in India due to aging populations and increased disease awareness. The lack of a cure makes comprehensive lifestyle management—combining medical intervention, nutrition, physical activity, and emotional care—essential for improved symptom control and optimal quality of life.
Understanding Parkinson’s Disease
PD manifests with motor symptoms such as tremor, rigidity, slowness, and balance problems, alongside non-motor issues including sleep disturbances, depression, and digestive troubles. Loss of dopamine-producing cells in key brain regions is responsible for these manifestations. Early diagnosis, often a challenge, allows for better intervention and patient outcomes.
Holistic Patient Support
Patients fare best when treatment integrates pharmacologic therapy, physiotherapy, occupational and speech interventions, and robust family and social support. In India, access to continuous care and community resources remains a challenge for many, but growing networks of clinics and support organizations are improving the landscape.
The Role of Diet: Indian Context
Diet is central to PD management. It can ease medication absorption, mitigate digestive symptoms, and promote brain health.
- Fibre-rich foods: Indian staples—whole grains like millets and brown rice, pulses, and fresh vegetables—combat constipation and stabilize blood sugar.
- Protein pacing: To optimize medication effectiveness, protein intake (curd, paneer, dal, fish, eggs) should be spaced away from dopaminergic drugs.
- Antioxidant sources: Traditional spices (turmeric, ginger, garlic), nuts, fresh fruits, and green tea help decrease inflammatory processes and support neural health.
- Adequate hydration: Sufficient water intake, herbal teas, and fruit juices help digestive motility and energy.
- Supplements: Vitamin D and calcium (via dairy, eggs, fortified cereals) support bone health, which is vital as falls become a risk.
Indian Diet Guidelines for Parkinson’s Disease
Physical Activity: Exercise, Movement, and Rehabilitation
Regular and progressive exercise preserves muscle tone, maintains balance, and boosts emotional resilience. Adapted exercise routines are crucial for mobility and fall prevention.
Preferable Activities
- Walking: 20–30 minutes daily, adapted for safety. Public parks and quiet lanes can provide secure settings.
- Yoga and stretching: Gentle asanas, pranayama (breathing exercises), and meditation calm tremors and reduce rigidity. Available in most Indian urban centers.
- Resistance/strength training: Using resistance bands or light weights, at least twice weekly, counters muscle wastage.
- Dance and music therapies: Indian folk dances (Garba, Bhangra), Bollywood-inspired movement, and rhythm therapies are enjoyable social activities.
- Physiotherapy: Individualized plans by certified therapists help with postural control, gait, and coordination.
Rehabilitation
Hydrotherapy, gait training, and occupational therapy programs are increasingly accessible in major hospitals. These offer structured movement, balance improvement, and strategies to maintain independence in daily activities.
Weekly Exercise Planner for Parkinson’s Disease
Medication and Surgical Options
Drug therapy remains the cornerstone of PD management. Indian clinicians use the following:
- Levodopa/Carbidopa: The gold standard for motor symptom relief.
- Dopamine agonists, anticholinergics, MAO-B and COMT inhibitors: Used alone or in combination for better control.
- Continuous infusion therapies: Apomorphine or Duodopa gel administered via pumps can help advanced cases with fluctuations.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): Surgical option for patients with drug-refractory symptoms, performed in major Indian neurology centers. It modulates neural circuits to improve movement.
Alternative and Complementary Medicine
Indian patients increasingly explore therapies such as:
- Ayurveda: Doctors prescribe herbal formulations and dietary adaptations believed to have neuroprotective effects.
- Yoga and Mindfulness: Gentle flow, meditative breathing, and lifestyle guidance improve flexibility and mind-body integration.
- Siddha, Unani, Homeopathy, TCM: Used as adjuncts to conventional care; their efficacy varies and is subject to ongoing research.
Always consult with a specialist before supplementing or altering prescribed therapies, as herb-drug interactions and false claims abound.
Daily Living and Emotional Wellness
Coping with PD in India requires adapting homes, social routines, and mental health practices.
- Safety at home: Install handrails, use non-slip mats in bathrooms, arrange furniture for easy passage, and remove trip hazards.
- Sleep hygiene: Stick to regular sleep schedules, avoid late caffeine, and incorporate relaxation rituals.
- Mental health: Engage in mindfulness, prayer, and cognitive practices. Seek help for depression, anxiety, or sleep problems.
- Family and caregiver support: Educate family, use community resources, and join Parkinson’s support groups for emotional, informational, and practical help.
Parkinson’s Daily Routine Checklist
Staying Up-to-Date: Clinical Advances in India
India is witnessing rapid advancements in PD care—new drugs, improved surgical techniques, rehabilitation programs, and telemedicine consults make expert help more accessible outside major metros. Public awareness campaigns, patient support foundations, and government initiatives are creating better-informed communities.
- Research: Clinical trials in India are testing newer drugs and integrated care models.
- Patient education: Ongoing resource development in local languages, digital platforms, and telehealth.
- Insurance and cost management: Expanded health insurance coverage and government schemes are making therapies more affordable.
You may also like : Dua Old Age Caring Institution, NRI Elder Parents Care